AAMI ST108: Redefining Water Quality Standards in Sterile Processing
Water is the most used—and often the most overlooked—substance in sterile processing. From cleaning and rinsing to disinfection and sterilization, water quality directly impacts patient safety, instrument integrity, and device performance. Recognizing this, the Association for the Advancement of Medical Instrumentation (AAMI) introduced ANSI/AAMI ST108:2023, a transformative standard that replaces the previous technical guideline, AAMI TIR34.
At Agenics Labs, we understand the critical role water plays in infection prevention and equipment performance. That’s why we’ve developed Agenics Affirm™, a suite of water testing solutions designed specifically to help healthcare facilities meet the rigorous demands of ST108 with ease and confidence.
ANSI/AAMI ST108 and Why it Matters
ANSI/AAMI ST108:2023 is the new consensus standard for water used in the processing of medical devices. It establishes guidelines for water quality, testing, monitoring, and system design in sterile processing departments (SPDs).
This standard is a significant evolution from AAMI TIR34, which served as a technical information report. With highly specific quality standards, ST108 is now enforceable by accrediting bodies such as The Joint Commission and DNV, making compliance not just a best practice but a regulatory necessity.
Why was this standard created? It has been established that poor water quality can have adverse effects on:
Patients: Increased risk of healthcare-associated infections (HAIs) due to microbial or endotoxin contamination.
Instruments: Corrosion, pitting, staining, and shortened lifespan.
Processes: Reduced effectiveness of detergents, biofilm buildup, and compromised sterilization.
Facilities: Increased maintenance costs and potential regulatory penalties.
But maintaining water quality to the standards set in ST108 significantly mitigates these common problems.
Need to Know Updates
While some elements reflect guidelines in AAMI TIR34, there are several specific areas that have been added or expanded on in ST108. Below is a quick overview of these areas.
1. The Three Categories of Water
ST108 defines and regulates three distinct water types:
Utility Water: The initial water coming into a healthcare facility, typically tap water. This water may require additional treatment to meet the quality requirements as outlined in the Standard and can be used for general cleaning tasks such as flushing, washing, and rinsing medical devices.
Critical Water: Extensively treated water that meets purity standards for steam generation and rinsing surgical instruments, ensuring patient safety by minimizing organic and inorganic contaminants, microorganisms, and endotoxins.
Steam: Water converted to vapor for sterilization. Must be tested as steam condensate to ensure purity.
2. Water Management Program
ST108 outlines the creation of a multi-disciplinary team responsible for every aspect of water quality management from generating the water, to monitoring it. Creating a cross-discipline team is essential to ensure organization buy-in and alignment. Different departments and individuals are likely to have varying levels of responsibility. Some will be involved with the water management program daily, while others may only need to review ongoing performance, still others may only be involved in the initial set-up phase.
Getting a team together should be the first step to ensure nothing (and no one) gets overlooked. Once the team is established, map out a plan of action specifying each member’s responsibilities as they pertain to the following tasks:
Risk assessments
System design and validation
Routine monitoring
Documentation
Performance monitoring and corrective actions
Standard operating procedures for every aspect of the program should be published and regularly reviewed.
3. Water Quality Testing Requirements
There are two general categories of testing requirements. The first, is called the Initial Qualification. ST108 details what must be evaluated for each water type including the test metric (such as bacteria, endotoxins, TOCs, etc.) and every location within the system that must be sampled (such as sample points within the water generation system and points of use).
The second category is Routine Monitoring. ST108 details what must be evaluated for each water type, which locations must be sampled, and the frequency at which the different water types must be tested.
Initial Qualification
When installing a water treatment system, extensive testing is needed to confirm the design produces water that meets all quality standards. Once these more rigorous requirements are consistently met, testing can be less frequent, but monitoring must continue. The Water Management Team should determine the initial frequency and quantity of qualification tests that must be performed (and meet the standards) to consider the system ‘qualified’. For example, the team may agree to obtain 3 consecutive weeks of passing results to confirm performance before transitioning to routine testing.
The following categories are included under qualification testing per the standard:
Microbial: Tests for heterotrophic bacteria and endotoxins.
Chemical: Checks for dissolved minerals and metals.
General Water Quality: Evaluates characteristics such as pH, total alkalinity, conductivity, turbidity, and total organic carbon (TOC).
Routine Monitoring
Once the Initial Qualification testing is satisfactorily completed, facilities may convert to Routine Monitoring. Fewer metrics are required in routine monitoring; however, the standard does specify specific testing intervals for each water type. Utility and Steam water should be tested quarterly, while Critical water should be tested monthly. Refer to the table below for testing parameters.
ST108 also specifies the locations of sampling that must be completed:
Water generation system (where treatment occurs)
Points of use (POUs) (where water contacts devices)
Steam systems (for sterilizers)
Four Steps to Achieve Compliance
1. Assess Current Water Systems and Water Quality
It may be possible to determine that some critical water treatment components are missing before even conducting a test. If unsure however, AffirmCritical+ and AffirmUtility+ can provide an initial assessment of a facility’s water quality to help identify gaps in water treatment. Such gaps may include components like UV lights to reduce bacteria or specialized filters to reduce endotoxins.
2. Implement a Water Management Plan
Identify all relevant parties within the organization who will be a part of the team. Based on the initial assessment, it is possible licensed plumbers and/or facilities professionals will need to make some of the system changes - which is precisely why a diverse Water Management Team is so important!
As a team, conduct a risk assessment to determine the specific requirements your organization will establish and uphold. Then, create a written protocol that includes plans for qualification, routine monitoring, and corrective action. With the system gaps identified and program objectives specified, begin implementing the necessary changes to the water treatment system(s).
3. Validate the New Systems
Follow the protocol developed to verify the new system produces water that passes the qualification standards of ST108. In addition to water quality, use this validation period to determine if the overall structure of the protocol is working. Review if all the relevant parties are involved and receiving appropriate updates. Determine if proper systems are in place to monitor the water quality results and respond to metrics that fall out of range.
4. Routinely Monitor Water Quality
Once the qualification and validation phase is complete, shift into routine monitoring. The specifics for testing are detailed in ST108 (and above in this blog). But your Water Management Plan will be the guide for who reviews the test results, what kind of KPI’s are tracked and reported on, and how frequently the team meets to review the results more broadly.
Any remedial action and routine maintenance should also be adhered to.
How Agenics Labs Makes it Easy
At Agenics Labs, we’ve developed a comprehensive solution to help healthcare professionals meet ST108 requirements without complexity.
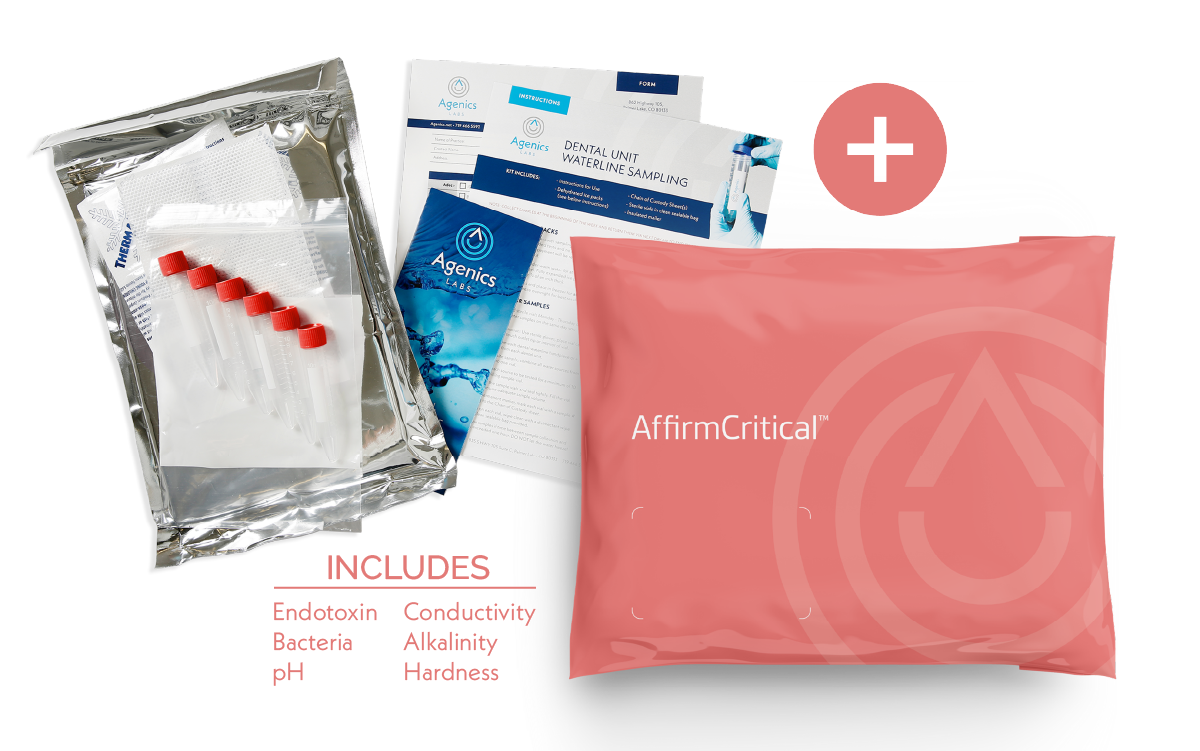
Our AffirmCritical™ and AffirmUtility™ kits are tailored specifically for ST108 water quality compliance and include the metrics required for each water type.
Each kit includes everything needed to collect and return water samples to our lab, so you don’t need to worry about sourcing appropriate materials:
Sterile collection vials
Prepaid overnight shipping
Insulated shipping materials
Sample submission form for sample tracking
Online results stored in our portal
Affirm Base kits provide the essential metrics of bacteria for Utility or bacteria and endotoxin for Critical. Affirm Plus kits provide expanded metrics of pH, Conductivity, Alkalinity, and Hardness.
Complete Testing in 4 Simple Steps!
No contracts, no hidden fees for results. The price you pay upfront includes everything from materials to results, allowing you control over your budgeting.
ST108 Readiness Resources
We provide:
ST108 Overview Guides
Submission Forms & IFUs
Water Management Guidance
Educational Webinars and Videos
Our team of water quality specialists work directly with sterile processing professionals to:
Interpret test results
Recommend corrective actions
Optimize water treatment protocols
Ensure audit readiness
Common Questions About ST108
-
All test results will be available online within 5 business days of sample receipt.
-
The standard is now considered Standard of Care for patient safety. Accrediting bodies like The Joint Commission and DNV now require adherence to ST108 as part of their infection control and quality standards. Most organizations receiving The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) funding will be subject to meet the requirements of ST108.
-
Monthly testing is recommended for Critical Water. Frequency may vary based on system design, usage, and risk assessments.
Quarterly testing is the standard recommendation for Utility water and Steam.
-
Agenics Labs provides corrective guidance and retesting support to help you quickly return to compliance. Remedial actions should be included in an organization’s Water Management Program protocols.
-
Toxic substances found in the outer membrane of certain bacteria, primarily Gram-negative bacteria. They are released when these bacteria die or break apart.
-
A documented plan required under ANSI/AAMI ST108 that outlines how dental and healthcare facilities monitor, control, and maintain water quality in their systems. It identifies risks, sets testing and treatment protocols, and ensures compliance to prevent microbial contamination and protect patient safety.
Final Thoughts
AAMI ST108 is more than a new standard—it’s a call to action for healthcare facilities to elevate their water quality practices. With Agenics Labs as your partner, compliance doesn’t have to be complicated. Our Affirm™ testing solutions, expert support, and educational resources make it easy to protect your patients, your instruments, and your reputation.
Let your confidence flow with Agenics Labs. Explore our ST108 testing kits and resources.
Why Choose Agenics Labs?
Healthcare-Focused: We specialize in water testing for sterile processing and dental waterlines.
Regulatory Expertise: Our protocols align with AAMI, CDC, and EPA standards.
Data-Driven: Our reports include actionable metrics like CFU counts, pH, TDS, and more.
Trusted by Professionals: From hospitals to outpatient centers, we’re the go-to partner for water quality assurance.
“The importance of monitoring water quality to prevent problems with microbial proliferation cannot be overemphasized.” — AAMI
Need help? Click the button below to send us a message.
-
Aami. (2023, August 16). New AAMI standard on water quality for medical device processing. AAMI. https://pressroom.aami.org/posts/news/new-aami-standard-on-water-quality-for-medica
Schirn, A. (2025, June 4). ANSI/AAMI ST108:2023- water for Processing Medical Devices - ANSI BLOG. The ANSI Blog. https://blog.ansi.org/ansi/ansi-aami-st108-2023-water-quality-medical-devices/
Editor, J. P. | S. (2025, April 1). Does your SPD meet water quality standards?. Outpatient Surgery Magazine. https://www.aorn.org/outpatient-surgery/article/does-your-spd-meet-water-quality-standards
ANSI/AAMI ST108 guide: Get chemready. ChemREADY. (2024, March 14). https://www.getchemready.com/ansi-aami-st108-standard-critical-water-systems/ansi-aami-st108-the-guide-to-water-quality-for-processing-of-medical-devices/
Frieders, B. (2025, November 26). Understanding AAMI ST108:2023: Essential Guide to new water quality standards in health care. Infection Control Today. https://www.infectioncontroltoday.com/view/understanding-aami-st108-2023-essential-guide-new-water-quality-standards-health-care